5.Rest风格
对于Rest风格,我们需要学习的内容包括:
- REST简介
- REST入门案例
- REST快速开发
- 案例:�基于RESTful页面数据交
REST简介
- REST(Representational State Transfer),表现形式状态转换,它是一种软件架构风格。当我们想表示一个网络资源的时候,可以使用两种方式:
- 传统风格资源描述形式
http://localhost/user/getById?id=1查询id为1的用户信息http://localhost/user/saveUser保存用户信息
- REST风格描述形式
http://localhost/user/1http://localhost/user
- 传统风格资源描述形式
传统方式一般是一个请求url对应一种操作,这样做不仅麻烦,也不安全,因为会程序的人读取了你的请求url地址,就大概知道该url实现的是一个什么样的操作。
查看REST风格的描述,你会发现请求地址变的简单了,并且光看请求URL并不是很能猜出来该URL的具体功能所以REST的优点有:
- 隐藏资源的访问行为,无法通过地址得知对资源是何种操作
- 书写简化
但是我们的问题也随之而来了,一个相同的url地址即可以是新增也可以是修改或者查询,那么到底我们该如何区分该请求到底是什么操作呢?
- 按照REST风格访问资源时使用行为动作区分对资源进行了何种操作
- http://localhost/users 查询全部用户信息 GET(查询)
- http://localhost/users/1 查询指定用户信息 GET(查询)
- http://localhost/users 添加用户信息 POST(新增/保存)
- http://localhost/users 修改用户信息 PUT(修改/更新)
- http://localhost/users/1 删除用户信息 DELETE(删除)
请求的方式比较多,但是比较常用的就4种,分别是GET , POST , PUT , DELETE。
按照不同的请求方式代表不同的操作类型。
- 发送GET请求是用来做查询
- 发送POST请求是用来做新增
- 发送PUT请求是用来做修改
- 发送DELETE请求是用来做删除
但是注意:
- 上述行为是约定方式,约定不是规范,可以打破,所以称REST风格,而不是REST规范
- REST提供了对应的架构方式,按照这种架构设计项目可以降低开发的复杂性,提高系统的可伸缩性
- REST中规定GET/POST/PUT/DELETE针对的是查询/新增/修改/删除,但是我们如果非要用GET请求做删除,这点在程序上运行是可以实现的
- 但是如果绝大多数人都遵循这种风格,你写的代码让别人读起来就有点莫名其妙了。
- 描述模块的名称通常使用复数,也就是加s的格式描述,表示此类资源,而非单个资源,例如:users、books、accounts......
清楚了什么是REST风格后,我们后期会经常提到一个概念叫RESTful,那什么又是RESTful呢?
- 根据REST风格对资源进行访问称为RESTful。
后期我们在进行开发的过程中,大多是都是遵从REST风格来访问我们的后台服务,所以可以说咱们以后都是基于RESTful来进行开发的。
RESTful入门案例
环境准备
-
创建一个Web的Maven项目
-
pom.xml添加Spring依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.itheima</groupId>
<artifactId>springmvc_06_rest</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.2.10.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.9.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat7-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.1</version>
<configuration>
<port>80</port>
<path>/</path>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project> -
创建对应的配置类
public class ServletContainersInitConfig extends
AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {
protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() {
return new Class[0];
}
protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() {
return new Class[]{SpringMvcConfig.class};
}
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[]{"/"};
}
//乱码处理
@Override
protected Filter[] getServletFilters() {
CharacterEncodingFilter filter = new CharacterEncodingFilter();
filter.setEncoding("UTF-8");
return new Filter[]{filter};
}
}
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.itheima.controller")
//开启json数据类型自动转换
@EnableWebMvc
public class SpringMvcConfig {
} -
编写模型类User和Book
public class User {
private String name;
private int age;
//getter...setter...toString省略
}
public class Book {
private String name;
private double price;
//getter...setter...toString省略
} -
编写UserController和BookController
@Controller
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("/save")
@ResponseBody
public String save(@RequestBody User user) {
System.out.println("user save..."+user);
return "{'module':'user save'}";
}
@RequestMapping("/delete")
@ResponseBody
public String delete(Integer id) {
System.out.println("user delete..." + id);
return "{'module':'user delete'}";
}
@RequestMapping("/update")
@ResponseBody
public String update(@RequestBody User user) {
System.out.println("user update..." + user);
return "{'module':'user update'}";
}
@RequestMapping("/getById")
@ResponseBody
public String getById(Integer id) {
System.out.println("user getById..." + id);
return "{'module':'user getById'}";
}
@RequestMapping("/findAll")
@ResponseBody
public String getAll() {
System.out.println("user getAll...");
return "{'module':'user getAll'}";
}
}
@Controller
public class BookController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/books",method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public String save(@RequestBody Book book){
System.out.println("book save..." + book);
return "{'module':'book save'}";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/books/{id}",method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
@ResponseBody
public String delete(@PathVariable Integer id){
System.out.println("book delete..." + id);
return "{'module':'book delete'}";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/books",method = RequestMethod.PUT)
@ResponseBody
public String update(@RequestBody Book book){
System.out.println("book update..." + book);
return "{'module':'book update'}";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/books/{id}",method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public String getById(@PathVariable Integer id){
System.out.println("book getById..." + id);
return "{'module':'book getById'}";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/books",method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public String getAll(){
System.out.println("book getAll...");
return "{'module':'book getAll'}";
}
}
最终创建好的项目结构如下:
思路分析
需求:将之前的增删改查替换成RESTful的开发方式。
1.之前不同的请求有不同的路径,现在要将其修改为统一的请求路径
- 修改前: 新增: /save ,修改: /update,删除 /delete...
- 修改后: 增删改查: /users
2.根据GET查询、POST新增、PUT修改、DELETE删除对方法的请求方式进行限定
3.发送请求的过程中如何设置请求参数?
修改RESTful风格
新增
@Controller
public class UserController {
//设置当前请求方法为POST,表示REST风格中的添加操作
@RequestMapping(value = "/users",method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public String save() {
System.out.println("user save...");
return "{'module':'user save'}";
}
}
- 将请求路径更改为/users
- 访问该方法使用 POST: http://localhost/users
- 使用method属性限定该方法的访问方式为POST
-
如果发送的不是POST请求,比如发送GET请求,则会报错
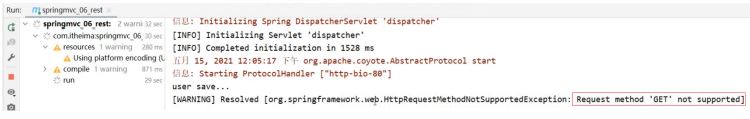
-
删除
@Controller
public class UserController {
//设置当前请求方法为DELETE,表示REST风格中的删除操作
@RequestMapping(value = "/users",method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
@ResponseBody
public String delete(Integer id) {
System.out.println("user delete..." + id);
return "{'module':'user delete'}";
}
}
- 将请求路径更改为/users
- 访问该方法使用 DELETE: http://localhost/users
访问成功,但是删除方法没有携带所要删除数据的 id,所以针对RESTful的开发,如何携带数据参数?
传递路径参数
前端发送请求的时候使用: http://localhost/users/1 ,路径中的1就是我们想要传递的参数。
后端获取参数,需要做如下修改:
- 修改@RequestMapping的value属性,将其中修改为
/users/{id},目的是和路径匹配 - 在方法的形参前添加@PathVariable注解
@Controller
public class UserController {
//设置当前请求方法为DELETE,表示REST风格中的删除操作
@RequestMapping(value = "/users/{id}",method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
@ResponseBody
public String delete(@PathVariable Integer id) {
System.out.println("user delete..." + id);
return "{'module':'user delete'}";
}
}
思考如下两个问题:
如果方法形参的名称和路径中的值不一致,该怎么办?

如果有多个参数需要传递该如何编写?
前端发送请求的时候使用: http://localhost/users/1/tom ,路径中的1和tom就是我们想要传递的两个参数。
后端获取参数,需要做如下修改:
@Controller
public class UserController {
//设置当前请求方法为DELETE,表示REST风格中的删除操作
@RequestMapping(value = "/users/{id}/{name}",method =
RequestMethod.DELETE)
@ResponseBody
public String delete(@PathVariable Integer id,@PathVariable String name)
{
System.out.println("user delete..." + id+","+name);
return "{'module':'user delete'}";
}
}
修改
@Controller
public class UserController {
//设置当前请求方法为PUT,表示REST风格中的修改操作
@RequestMapping(value = "/users",method = RequestMethod.PUT)
@ResponseBody
public String update(@RequestBody User user) {
System.out.println("user update..." + user);
return "{'module':'user update'}";
}
}
-
将请求路径更改为/users
- 访问该方法使用 PUT: http://localhost/users
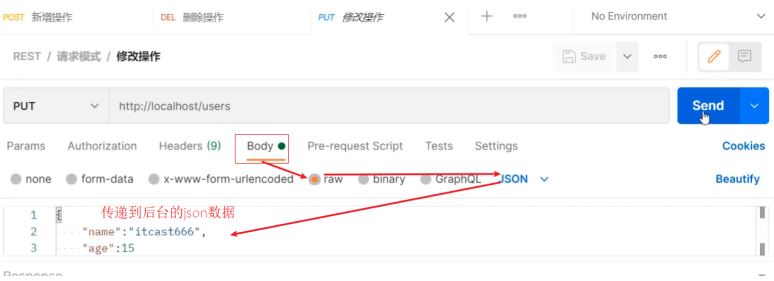
-
访问并携带参数:
根据ID查询
@Controller
public class UserController {
//设置当前请求方法为GET,表示REST风格中的查询操作
@RequestMapping(value = "/users/{id}" ,method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public String getById(@PathVariable Integer id){
System.out.println("user getById..."+id);
return "{'module':'user getById'}";
}
}
将请求路径更改为/users
- 访问该方法使用 GET: http://localhost/users/666
查询所有
@Controller
public class UserController {
//设置当前请求方法为GET,表示REST风格中的查询操作
@RequestMapping(value = "/users" ,method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public String getAll() {
System.out.println("user getAll...");
return "{'module':'user getAll'}";
}
}
将请求路径更改为/users
- 访问该方法使用 GET: http://localhost/users
小结
RESTful入门案例,我们需要学习的内容如下:
设定Http请求动作(动词)
@RequestMapping(value="",method = RequestMethod.POST|GET|PUT|DELETE)
设定请求参数(路径变量)
@RequestMapping(value="/users/{id}",method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
@ReponseBody
public String delete(@PathVariable Integer id){
}
知识点1:@PathVariable
| 名称 | @PathVariable |
|---|---|
| 类型 | 形参注解 |
| 位置 | SpringMVC控制器方法形参定义前面 |
| 作用 | 绑定路径参数与处理器方法形参间的关系,要求路径参数名与形参名一一对应 |
关于接收参数,我们学过三个注解@RequestBody、@RequestParam、@PathVariable ,这三个注之间的区别和应用分别是什么?
- 区别
- @RequestParam用于接收url地址传参或表单传参
- @RequestBody用于接收json数据
- @PathVariable用于接收路径参数,使用
{参数名称}描述路径参数
- 应用
- 后期开发中,发送请求参数超过1个时,以json格式为主,@RequestBody应用较广
- 如果发送非json格式数据,选用@RequestParam接收请求参数
- 采用RESTful进行开发,当参数数量较少时,例如1个,可以采用@PathVariable接收请求路径变量,通常用于传递id值
RESTful快速开发
做完了RESTful的开发,你会发现好麻烦,麻烦在哪?
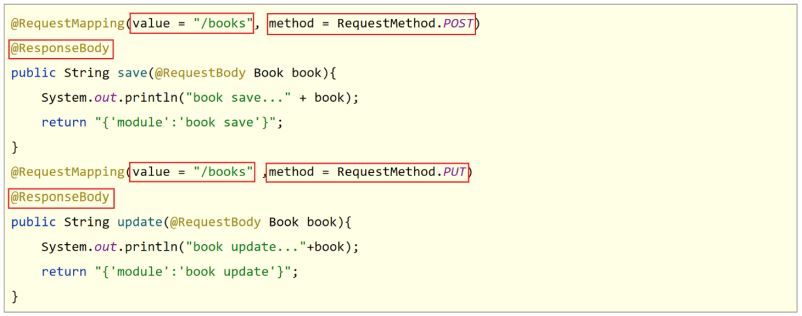
- 问题1:每个方法的@RequestMapping注解中都定义了访问路径/books,重复性太高。
- 问题2:每个方法的@RequestMapping注解中都要使用method属性定义请求方式,重复性太高。
- 问题3:每个方法响应json都需要加上@ResponseBody注解,重复性太高。
对于上面所提的这三个问题,具体该如何解决?
@RestController //@Controller + ReponseBody
@RequestMapping("/books")
public class BookController {
//@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
@PostMapping
public String save(@RequestBody Book book){
System.out.println("book save..." + book);
return "{'module':'book save'}";
}
//@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}",method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
@DeleteMapping("/{id}")
public String delete(@PathVariable Integer id){
System.out.println("book delete..." + id);
return "{'module':'book delete'}";
}
//@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.PUT)
@PutMapping
public String update(@RequestBody Book book){
System.out.println("book update..." + book);
return "{'module':'book update'}";
}
//@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}",method = RequestMethod.GET)
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public String getById(@PathVariable Integer id){
System.out.println("book getById..." + id);
return "{'module':'book getById'}";
}
//@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
@GetMapping
public String getAll(){
System.out.println("book getAll...");
return "{'module':'book getAll'}";
}
}
对于刚才的问题,我们都有对应的解决方案:
问题1:每个方法的@RequestMapping注解中都定义了访问路径/books,重复性太高。
- 将@RequestMapping提到类上面,用来定义所有方法共同的访问路径。
问题2:每个方法的@RequestMapping注解中都要使用method属性定义请求方式,重复性太高。
- 使用@GetMapping @PostMapping @PutMapping @DeleteMapping代替
问题3:每个方法响应json都需要加上@ResponseBody注解,重复性太高。
- 将ResponseBody提到类上面,让所有的方法都有@ResponseBody的功能
- 使用@RestController注解替换@Controller与@ResponseBody注解,简化书写
知识点1:@RestController
| 名称 | @RestController |
|---|---|
| 类型 | 类注解 |
| 位置 | 基于SpringMVC的RESTful开发控制器类定义上方 |
| 作用 | 设置当前控制器类为RESTful风格, 等同于@Controller与@ResponseBody两个注解组合功能 |
知识点2:@GetMapping @PostMapping @PutMapping @DeleteMapping
| 名称 | @GetMapping @PostMapping @PutMapping @DeleteMapping |
|---|---|
| 类型 | 方法注解 |
| 位置 | 基于SpringMVC的RESTful开发控制器方法定义上方 |
| 作用 | 设置当前控制器方法请求访问路径与请求动作,每种对应一个请求动作, 例如@GetMapping对应GET请求 |
| 相关属性 | value(默认):请求访问路径 |
RESTful案例
需求分析
需求一:图片列表查询,从后台返回数据,将数据展示在页面上
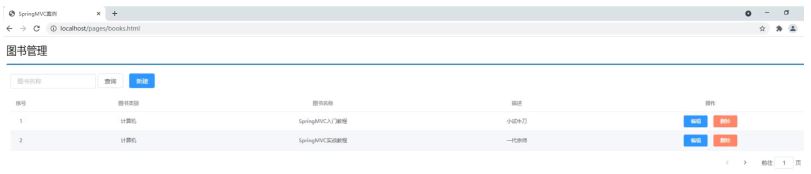
需求二:新增图片,将新增图书的数据传递到后台,并在控制台打印
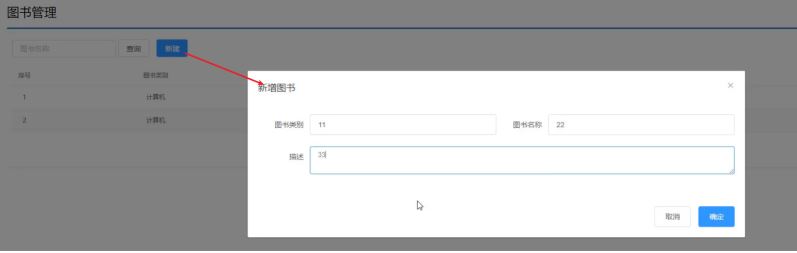
说明:此次案例的重点是在SpringMVC中如何使用RESTful实现前后台交互,所以本案例并没有和数据库进行交互,所有数据使用假数据来完成开发。
步骤分析
- 搭建项目导入jar包
- 编写Controller类,提供两个方法,一个用来做列表查询,一个用来做新增
- 在方法上使用RESTful进行路径设置
- 完成请求、参数的接收和结果的响应
- 使用PostMan进行测试
- 将前端页面拷贝到项目中
- 页面发送ajax请求
- 完成页面数据的展示
环境准备
-
创建一个Web的Maven项目
-
pom.xml添加Spring依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.itheima</groupId>
<artifactId>springmvc_07_rest_case</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.2.10.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.9.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat7-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.1</version>
<configuration>
<port>80</port>
<path>/</path>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project> -
创建对应的配置类
public class ServletContainersInitConfig extends
AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {
protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() {
return new Class[0];
}
protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() {
return new Class[]{SpringMvcConfig.class};
}
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[]{"/"};
}
//乱码处理
@Override
protected Filter[] getServletFilters() {
CharacterEncodingFilter filter = new CharacterEncodingFilter();
filter.setEncoding("UTF-8");
return new Filter[]{filter};
}
}
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.itheima.controller")
//开启json数据类型自动转换
@EnableWebMvc
public class SpringMvcConfig {
} -
编写模型类Book
public class Book {
private Integer id;
private String type;
private String name;
private String description;
//setter...getter...toString略
} -
编写BookController
@Controller
public class BookController {
}
最终创建好的项目结构如下:

后台接口开发
步骤1:编写Controller类并使用RESTful进行配置
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/books")
public class BookController {
@PostMapping
public String save(@RequestBody Book book){
System.out.println("book save ==> "+ book);
return "{'module':'book save success'}";
}
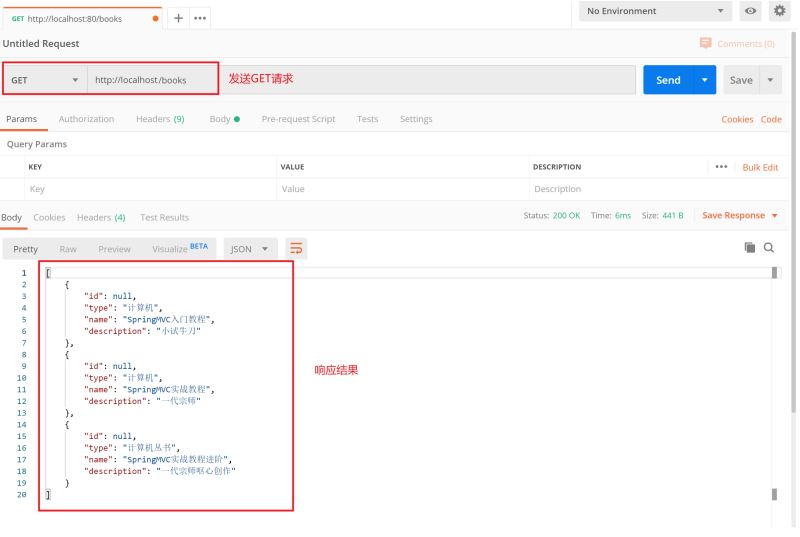
@GetMapping
public List<Book> getAll(){
System.out.println("book getAll is running ...");
List<Book> bookList = new ArrayList<Book>();
Book book1 = new Book();
book1.setType("计算机");
book1.setName("SpringMVC入门教程");
book1.setDescription("小试牛刀");
bookList.add(book1);
Book book2 = new Book();
book2.setType("计算机");
book2.setName("SpringMVC实战教程");
book2.setDescription("一代宗师");
bookList.add(book2);
Book book3 = new Book();
book3.setType("计算机丛书");
book3.setName("SpringMVC实战教程进阶");
book3.setDescription("一代宗师呕心创作");
bookList.add(book3);
return bookList;
}
}
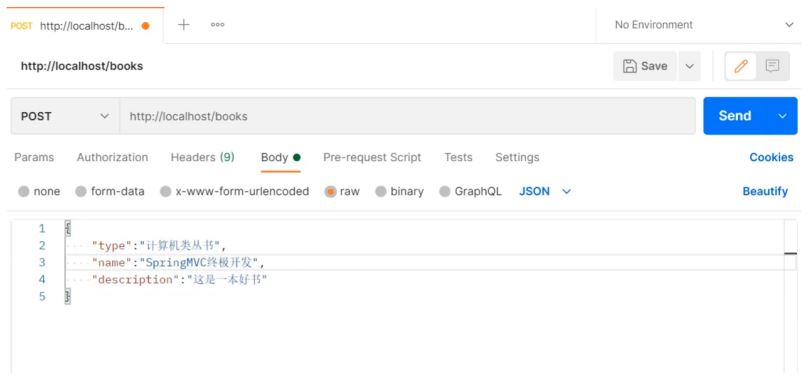
步骤2:使用PostMan进行测试
测试新增
{
"type":"计算机丛书",
"name":"SpringMVC终极开发",
"description":"这是一本好书"
}
测试查询
页面访问处理
步骤1:拷贝静态页面
将静态功能页面下的所有内容拷贝到项目的webapp目录下。
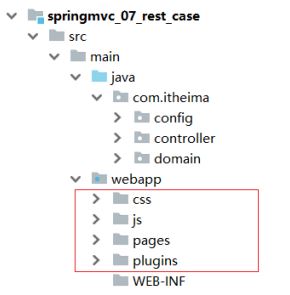
步骤2:访问pages目录下的books.html
打开浏览器输入http://localhost/pages/books.html
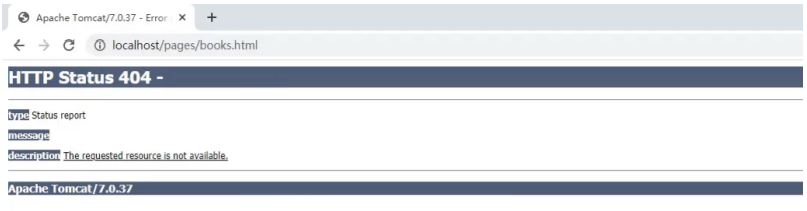
出现错误的原因?
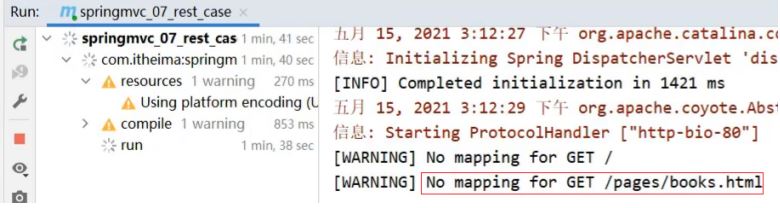
SpringMVC拦截了静态资源,根据/pages/books.html去controller找对应的方法,找不到所以会报404的错误。
SpringMVC为什么会拦截静态资源呢?
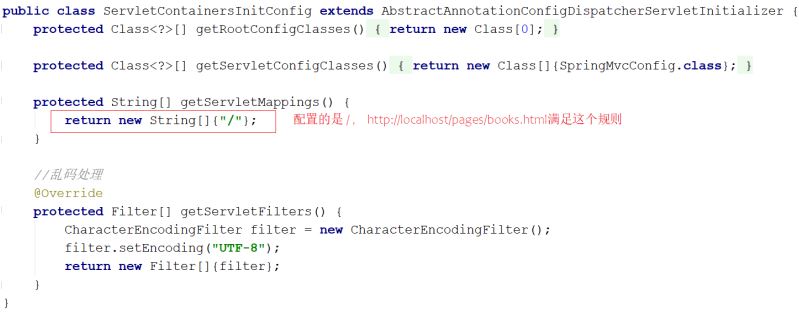
解决方案?
-
SpringMVC需要将静态资源进行放行。
@Configuration
public class SpringMvcSupport extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {
//设置静态资源访问过滤,当前类需要设置为配置类,并被扫描加载
@Override
protected void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
//当访问/pages/????时候,从/pages目录下查找内容
registry.addResourceHandler("/pages/**").addResourceLocations("/pages/");
registry.addResourceHandler("/js/**").addResourceLocations("/js/");
registry.addResourceHandler("/css/**").addResourceLocations("/css/");
registry.addResourceHandler("/plugins/**").addResourceLocations("/plugins/")
;
}
} -
该配置类是在config目录下,SpringMVC扫描的是controller包,所以该配置类还未生效,要想生效需要将SpringMvcConfig配置类进行修改
@Configuration
@ComponentScan({"com.itheima.controller","com.itheima.config"})
@EnableWebMvc
public class SpringMvcConfig {
}
或者
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.itheima")
@EnableWebMvc
public class SpringMvcConfig {
}
步骤3:修改books.html页面
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<!-- 页面meta -->
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>SpringMVC案例</title>
<!-- 引入样式 -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="../plugins/elementui/index.css">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="../plugins/font-awesome/css/fontawesome.min.css">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="../css/style.css">
</head>
<body class="hold-transition">
<div id="app">
<div class="content-header">
<h1>图书管理</h1>
</div>
<div class="app-container">
<div class="box">
<div class="filter-container">
<el-input placeholder="图书名称" style="width:
200px;" class="filter-item"></el-input>
<el-button class="dalfBut">查询</el-button>
<el-button type="primary" class="butT"
@click="openSave()">新建</el-button>
</div>
<el-table size="small" current-row-key="id"
:data="dataList" stripe highlight-current-row>
<el-table-column type="index" align="center"
label="序号"></el-table-column>
<el-table-column prop="type" label="图书类别"
align="center"></el-table-column>
<el-table-column prop="name" label="图书名称"
align="center"></el-table-column>
<el-table-column prop="description" label="描述"
align="center"></el-table-column>
<el-table-column label="操作" align="center">
<template slot-scope="scope">
<el-button type="primary" size="mini">编辑
</el-button>
<el-button size="mini" type="danger">删除
</el-button>
</template>
</el-table-column>
</el-table>
<div class="pagination-container">
<el-pagination
class="pagiantion"
@current-change="handleCurrentChange"
:current-page="pagination.currentPage"
:page-size="pagination.pageSize"
layout="total, prev, pager, next, jumper"
:total="pagination.total">
</el-pagination>
</div>
<!-- 新增标签弹层 -->
<div class="add-form">
<el-dialog title="新增图书"
:visible.sync="dialogFormVisible">
<el-form ref="dataAddForm" :model="formData"
:rules="rules" label-position="right" label-width="100px">
<el-row>
<el-col :span="12">
<el-form-item label="图书类别"
prop="type">
<el-input vmodel="formData.type"/>
</el-form-item>
</el-col>
<el-col :span="12">
<el-form-item label="图书名称"
prop="name">
<el-input vmodel="formData.name"/>
</el-form-item>
</el-col>
</el-row>
<el-row>
<el-col :span="24">
<el-form-item label="描述">
<el-input vmodel="formData.description" type="textarea"></el-input>
</el-form-item>
</el-col>
</el-row>
</el-form>
<div slot="footer" class="dialog-footer">
<el-button @click="dialogFormVisible =
false">取消</el-button>
<el-button type="primary"
@click="saveBook()">确定</el-button>
</div>
</el-dialog>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
<!-- 引入组件库 -->
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
<script src="../plugins/elementui/index.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script src="../js/axios-0.18.0.js"></script>
<script>
var vue = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data:{
dataList: [],//当前页要展示的分页列表数据
formData: {},//表单数据
dialogFormVisible: false,//增加表单是否可见
dialogFormVisible4Edit:false,//编辑表单是否可见
pagination: {},//分页模型数据,暂时弃用
},
//钩子函数,VUE对象初始化完成后自动执行
created() {
this.getAll();
},
methods: {
// 重置表单
resetForm() {
//清空输入框
this.formData = {};
},
// 弹出添加窗口
openSave() {
this.dialogFormVisible = true;
this.resetForm();
},
//添加
saveBook () {
axios.post("/books",this.formData).then((res)=>{
});
},
//主页列表查询
getAll() {
axios.get("/books").then((res)=>{
this.dataList = res.data;
});
},
}
})
</script>
</html>