5.数据结构-队列
队列
概述
计算机科学中,queue 是以顺序的方式维护的一组数据集合,在一端添加数据,从另一端移除数据。习惯来说,添加的一端称为尾,移除的一端称为头,就如同生活中的排队买商品
In computer science, a queue is a collection of entities that are maintained in a sequence and can be modified by the addition of entities at one end of the sequence and the removal of entities from the other end of the sequence
先定义一个简化的队列接口
public interface Queue<E> {
/**
* 向队列尾插入值
* @param value 待插入值
* @return 插入成功返回 true, 插入失败返回 false
*/
boolean offer(E value);
/**
* 从对列头获取值, 并移除
* @return 如果队列非空返回对头值, 否则返回 null
*/
E poll();
/**
* 从对列头获取值, 不移除
* @return 如果队列非空返回对头值, 否则返回 null
*/
E peek();
/**
* 检查队列是否为空
* @return 空返回 true, 否则返回 false
*/
boolean isEmpty();
/**
* 检查队列是否已满
* @return 满返回 true, 否则返回 false
*/
boolean isFull();
}
链表实现
下面以单向环形带哨兵链表方式来实现队列
代码
public class LinkedListQueue<E>
implements Queue<E>, Iterable<E> {
private static class Node<E> {
E value;
Node<E> next;
public Node(E value, Node<E> next) {
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}
private Node<E> head = new Node<>(null, null);
private Node<E> tail = head;
private int size = 0;
private int capacity = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
{
tail.next = head;
}
public LinkedListQueue() {
}
public LinkedListQueue(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
}
@Override
public boolean offer(E value) {
if (isFull()) {
return false;
}
Node<E> added = new Node<>(value, head);
tail.next = added;
tail = added;
size++;
return true;
}
@Override
public E poll() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
Node<E> first = head.next;
head.next = first.next;
if (first == tail) {
tail = head;
}
size--;
return first.value;
}
@Override
public E peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
return head.next.value;
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return head == tail;
}
@Override
public boolean isFull() {
return size == capacity;
}
@Override
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Iterator<E>() {
Node<E> p = head.next;
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return p != head;
}
@Override
public E next() {
E value = p.value;
p = p.next;
return value;
}
};
}
}
环形数组实现
好处
- 对比普通数组,起点和终点更为自由,不用考虑数据移动
- “环”意味着不会存在【越界】问题
- 数组性能更佳
- 环形数组比较适合实现有界队列、RingBuffer 等
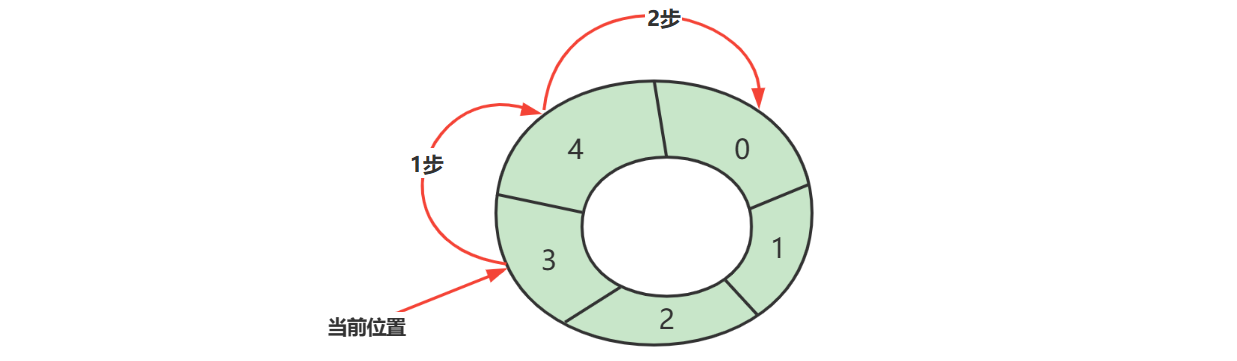
下标计算
例如,数组长度是 5,当前位置是 3 ,向前走 2 步,此时下标为 (3 + 2)\%5 = 0
(cur + step) \% length
- cur 当前指针位置
- step 前进步数
- length 数组长度
注意:
- 如果 step = 1,也就是一次走一步,可以在 >= length 时重�置为 0 即可
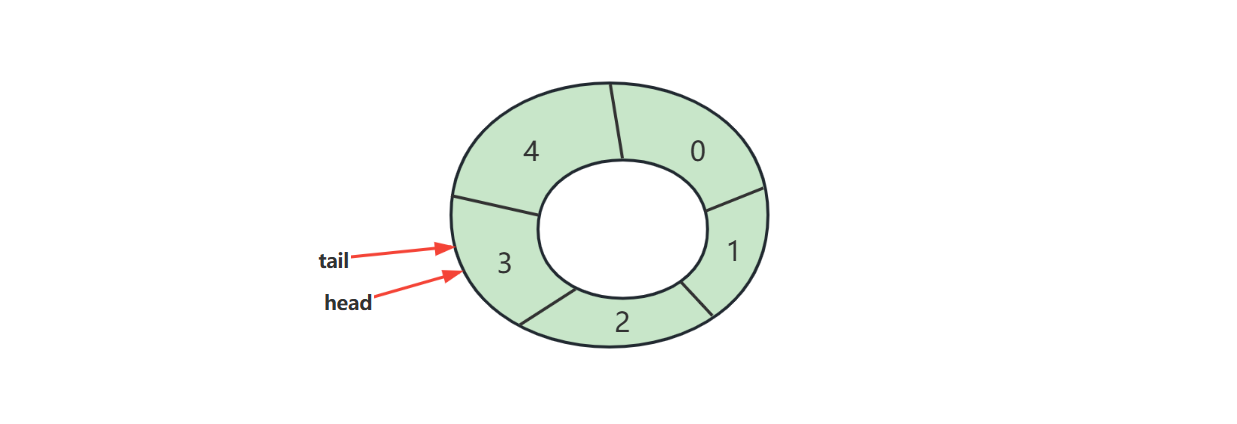
判断空
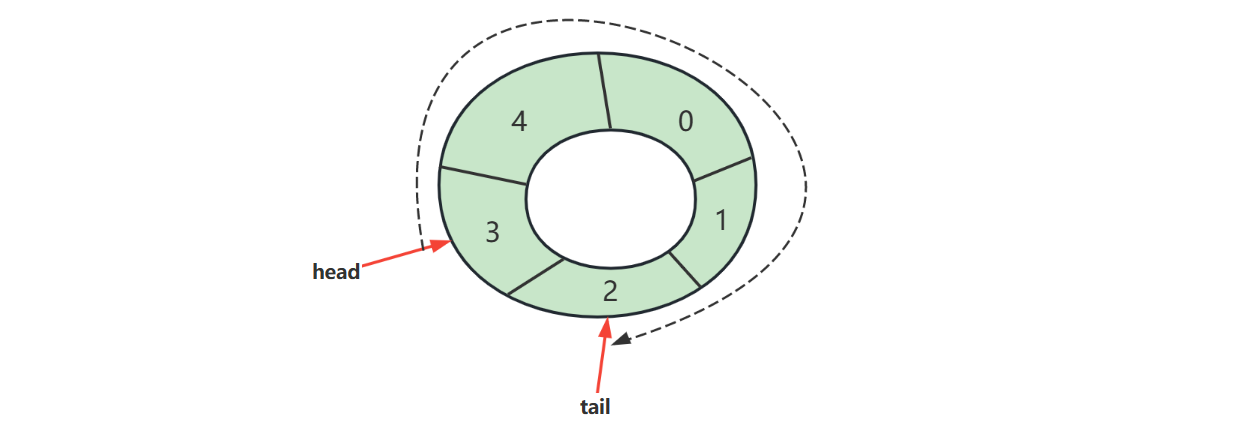
判断满
满之后的策略可以根据业务需求决定
- 例如我们要实现的环形队列,满之后就拒绝入队
代码
public class ArrayQueue<E> implements Queue<E>, Iterable<E>{
private int head = 0;
private int tail = 0;
private final E[] array;
private final int length;
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public ArrayQueue(int capacity) {
length = capacity + 1;
array = (E[]) new Object[length];
}
@Override
public boolean offer(E value) {
if (isFull()) {
return false;
}
array[tail] = value;
tail = (tail + 1) % length;
return true;
}
@Override
public E poll() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
E value = array[head];
head = (head + 1) % length;
return value;
}
@Override
public E peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
return array[head];
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return tail == head;
}
@Override
public boolean isFull() {
return (tail + 1) % length == head;
}
@Override
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Iterator<E>() {
int p = head;
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return p != tail;
}
@Override
public E next() {
E value = array[p];
p = (p + 1) % array.length;
return value;
}
};
}
}
判断空、满方法2
引入 size
public class ArrayQueue2<E> implements Queue<E>, Iterable<E> {
private int head = 0;
private int tail = 0;
private final E[] array;
private final int capacity;
private int size = 0;
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public ArrayQueue2(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
array = (E[]) new Object[capacity];
}
@Override
public boolean offer(E value) {
if (isFull()) {
return false;
}
array[tail] = value;
tail = (tail + 1) % capacity;
size++;
return true;
}
@Override
public E poll() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
E value = array[head];
head = (head + 1) % capacity;
size--;
return value;
}
@Override
public E peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
return array[head];
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
@Override
public boolean isFull() {
return size == capacity;
}
@Override
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Iterator<E>() {
int p = head;
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return p != tail;
}
@Override
public E next() {
E value = array[p];
p = (p + 1) % capacity;
return value;
}
};
}
}
判断空、满方法3
-
head 和 tail 不断递增,用到索引时,再用它们进行计算,两个问题
- 如何保证 head 和 tail 自增超过正整数最大值的正确性
- 如何让取模运算性能更高
-
答案:让 capacity 为 2 的幂
public class ArrayQueue3<E> implements Queue<E>, Iterable<E> {
private int head = 0;
private int tail = 0;
private final E[] array;
private final int capacity;
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public ArrayQueue3(int capacity) {
if ((capacity & capacity - 1) != 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("capacity 必须为 2 的幂");
}
this.capacity = capacity;
array = (E[]) new Object[this.capacity];
}
@Override
public boolean offer(E value) {
if (isFull()) {
return false;
}
array[tail & capacity - 1] = value;
tail++;
return true;
}
@Override
public E poll() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
E value = array[head & capacity - 1];
head++;
return value;
}
@Override
public E peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
return array[head & capacity - 1];
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return tail - head == 0;
}
@Override
public boolean isFull() {
return tail - head == capacity;
}
@Override
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Iterator<E>() {
int p = head;
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return p != tail;
}
@Override
public E next() {
E value = array[p & capacity - 1];
p++;
return value;
}
};
}
}
习题
E01. 二叉树层序遍历-Leetcode 102
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null) {
return result;
}
LinkedListQueue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedListQueue<>();
queue.offer(root);
int c1 = 1; // 本层节点个数
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int c2 = 0; // 下层节点个数
List<Integer> level = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < c1; i++) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
level.add(node.val);
if (node.left != null) {
queue.offer(node.left);
c2++;
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.offer(node.right);
c2++;
}
}
c1 = c2;
result.add(level);
}
return result;
}
// 自定义队列
static class LinkedListQueue<E> {
private static class Node<E> {
E value;
Node<E> next;
public Node(E value, Node<E> next) {
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}
private final Node<E> head = new Node<>(null, null);
private Node<E> tail = head;
int size = 0;
private int capacity = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
{
tail.next = head;
}
public LinkedListQueue() {
}
public LinkedListQueue(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
}
public boolean offer(E value) {
if (isFull()) {
return false;
}
Node<E> added = new Node<>(value, head);
tail.next = added;
tail = added;
size++;
return true;
}
public E poll() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
Node<E> first = head.next;
head.next = first.next;
if (first == tail) {
tail = head;
}
size--;
return first.value;
}
public E peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
return head.next.value;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return head == tail;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return size == capacity;
}
}
}
Ex1. 设计队列-Leetcode 622
由于与课堂例题差别不大,这里只给出参考解答
基于链表的实现
public class Ex1Leetcode622 {
private static class Node {
int value;
Node next;
Node(int value, Node next) {
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}
private final Node head = new Node(-1, null);
private Node tail = head;
private int size = 0;
private int capacity = 0;
{
tail.next = head;
}
public Ex1Leetcode622(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
}
public boolean enQueue(int value) {
if(isFull()) {
return false;
}
Node added = new Node(value, head);
tail.next = added;
tail = added;
size++;
return true;
}
public boolean deQueue() {
if(isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
Node first = head.next;
head.next = first.next;
if (first == tail) {
tail = head;
}
size--;
return true;
}
public int Front() {
if(isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
return head.next.value;
}
public int Rear() {
if(isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
return tail.value;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return head == tail;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return size == capacity;
}
}
注意:
- Leetcode 的实现里 deQueue(出队)返回值是布尔值,并不会返回队头元素
- 它期望用法是先用 Front 返回对头元素,再 deQueue 出队